- A virtual LAN or VLAN is a logical isolated network within a physical network. The idea is to create private networks for groups of virtual machines so they can share information between them without the risk of exposing the privacy of their data to machines outside the same VLAN.
- By creating a VLAN and adding Virtual Machines to it, they will have access to services such as shared storage, VPN management and connection to external networks.
- VLANs can traverse Cloud-Bricks physical servers, providing transparent connectivity for virtual machines running on different hardware nodes.
IPv4 and IPv6
- Private VLAN IP addresses within Cloud-Bricks belong to the 10.x.x.x (IPv4) and fd00 :: (IPv6) networks.
- Each vLAN automatically receives a segment of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. Such addresses are managed by the Cloud-Bricks system to avoid repeated assignments.
Creating a VLAN
Navigate to "Networking> VLANs" in the left menu.

Click on the "Create VLAN..." button and assign a name to the VLAN.
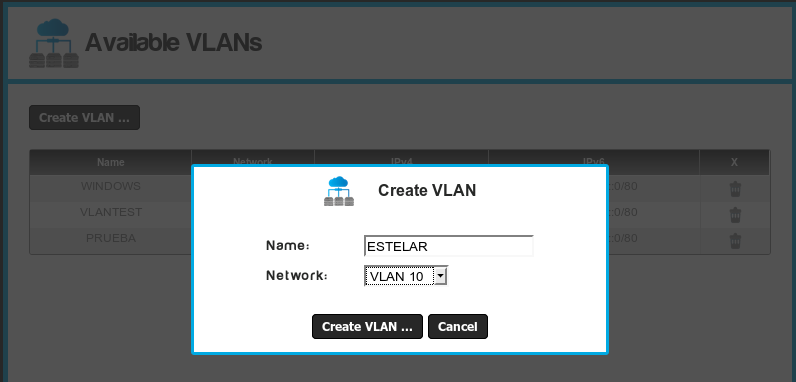
- Write the name of the VLAN and select a network number.
- The VLAN number will define the network segment assigned to
it.
For example for VLAN 10, the network segment will be 10.X.10.0/24.
- Then click on the "Create VLAN..." button and the VLAN will be added.
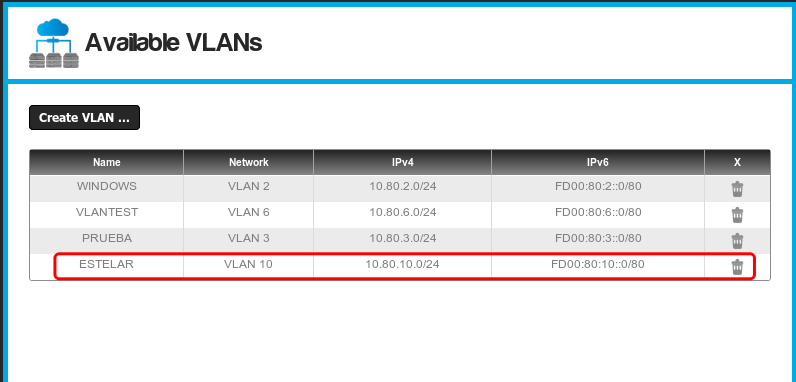
- As you can see, both IPv4 and IPv6 networks are created.
- The VLANs are now available for virtual machines, storage and VPN connections.
Assign virtual machines to VLANs
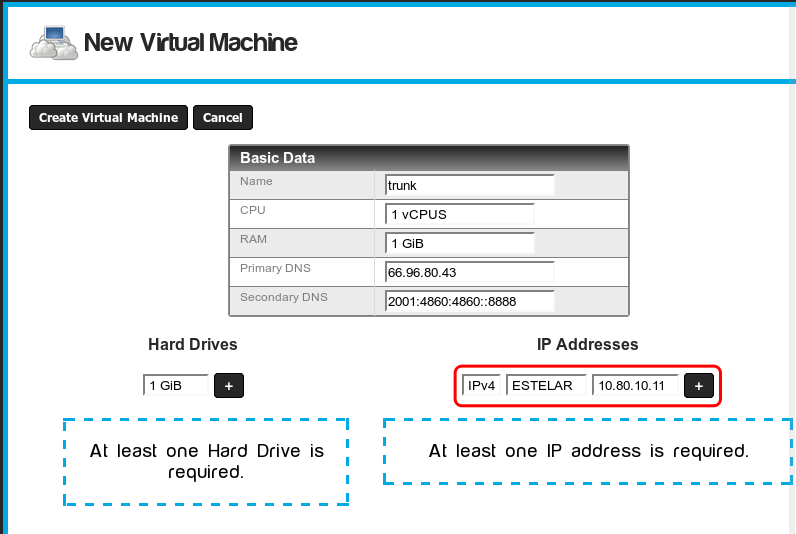
Now you should create a new virtual machine or modify an existing one by adding an IP address of the VLAN you just created.
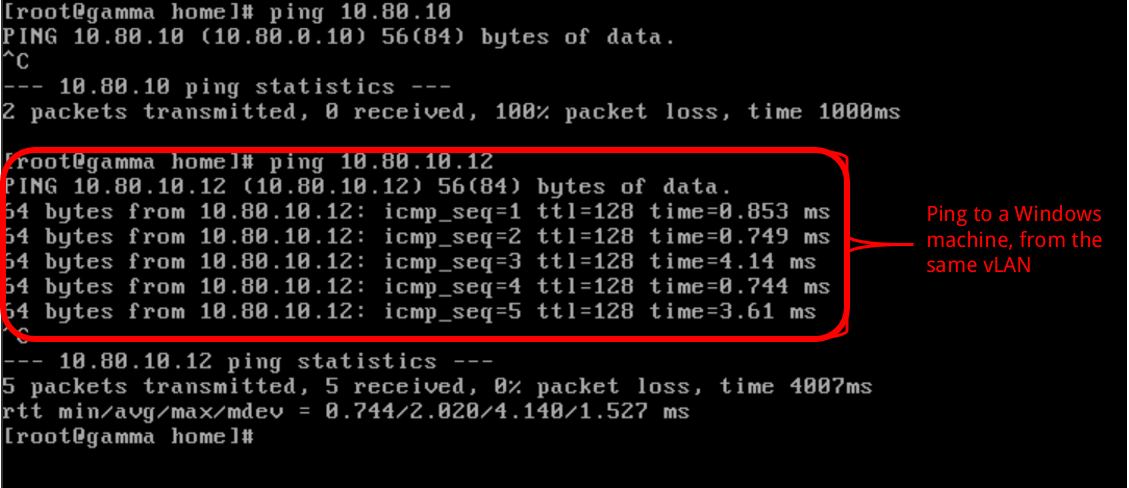
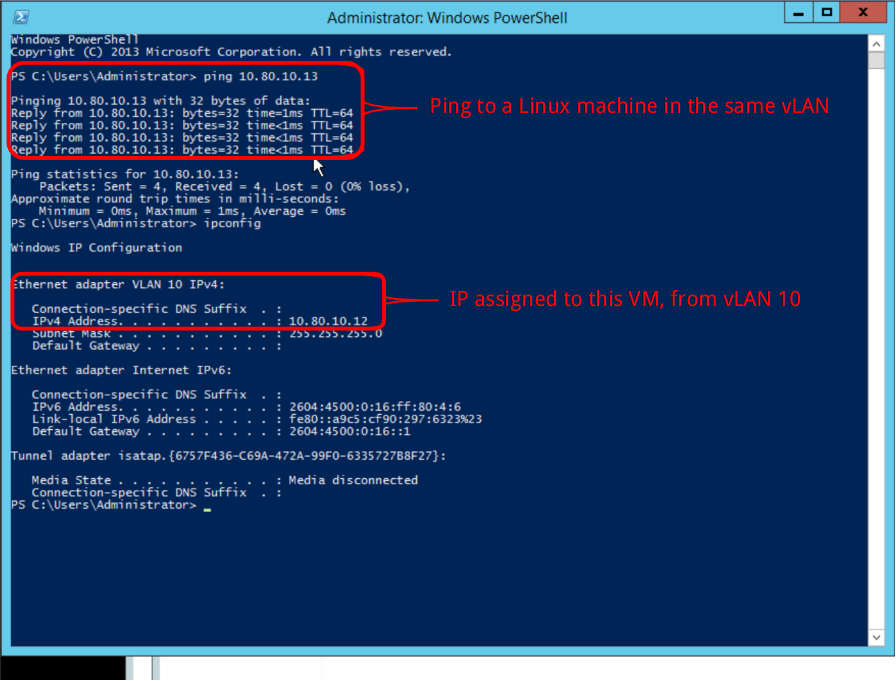
When two or more virtual machines belong to the same VLAN they are able to communicate to each other via any IP protocol.
In the following example, two virtual machines belong to the same VLAN (name "Estelar"), and it is possible to run pings between them.
- On Windows:
- On Linux