
The objects created in this table can later be used when Creating Firewall Rules for Virtual Machines.
Supported protocols
When you create a firewall service, you can select between
different protocols:
- TCP: Is one of the main protocols in the Internet and
Intranets. Whereas the IP protocol deals only with packets, TCP
enables two hosts to establish a connection and exchange streams
of data. TCP guarantees delivery of data and also guarantees
that packets will be delivered in the same order in which they
were sent. Example: Email, Web Browsing , FTP, etc.
- UDP: Uses a simple connection-less transmission model with a
minimum of protocol overhead. There is no guarantee of delivery,
ordering, or duplicate protection. Example: VoIP, Streaming,
DNS, SNMP, etc.
- ICMP: It is used by network devices, like routers, to send
error or network tracing information. ICMP can also be used to
relay query messages. It uses protocol numbers ICMP instead of
ports.
- ICMP-v6: It is the IPv6 version of ICMP.
Some services may send information using both TCP and UDP.
Create a firewall service/object
Navigate to "Firewall>Services" on the left menu.
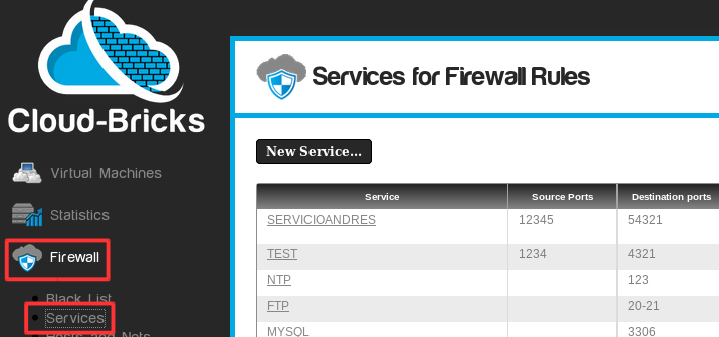
Click on the "New Service..." button and fill in the service configuration parameters.
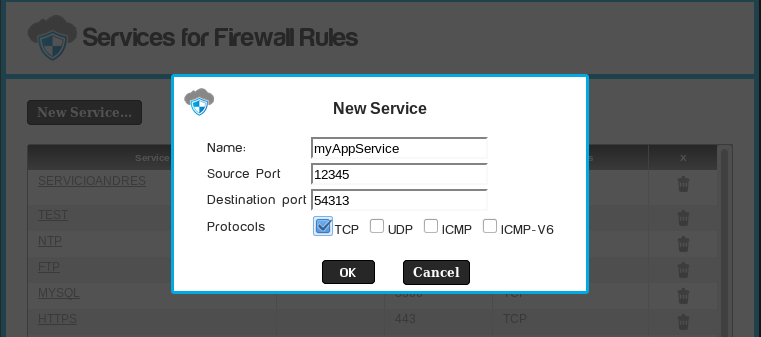
Click on "OK" and then "Commit Changes".
Create service using port ranges
- Firewall rules base their operations in ports, you can restrict access to specific ports or port ranges.
- For example, we can create a rule for FTP service using TCP
ports 21 to 22.
- Use a dash "-" to indicate a port range.
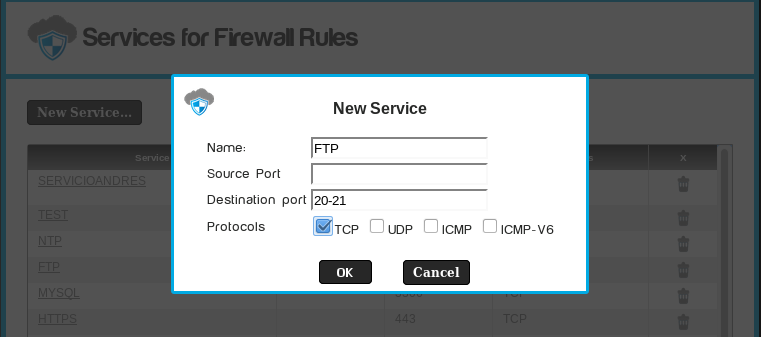
You may create a service using an ICMP-v6 number list.

- You may also create a service with for different ports,
separated by ","
- For example a tomcat web server running on different ports:
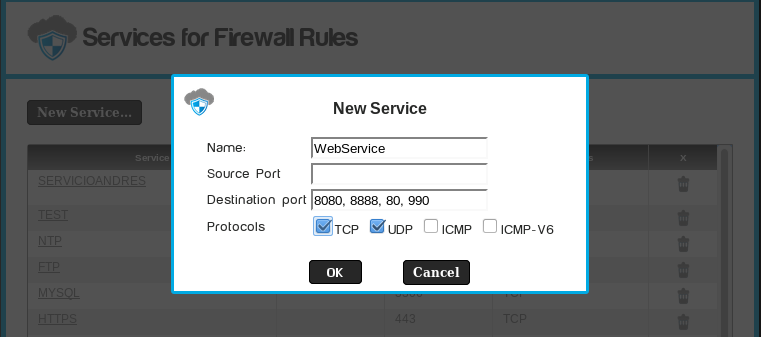
You may also use port ranges (-) and different port numbers (,) also for the source port field.